Water Analysis
Water
Water Analysis
Water is life. It directly sustains humankind and its developmental needs. Water plays infinite roles in our day to day life with abundant applications. According to the specific end use of water, one needs to set its desirable characteristics. Here we enlist a few applications that need certain quality parameters to be tested. Boiler water
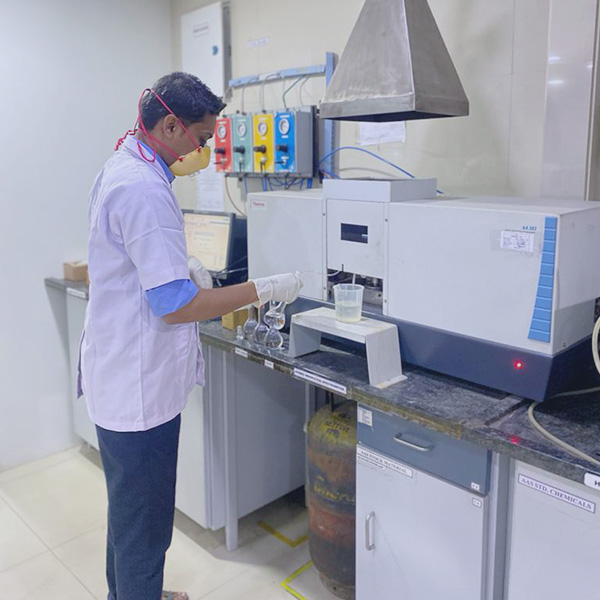

To ensure that a boiler runs properly over its lifetime, treating the water that circulates within the system is important. In absence of desired quality of boiler water and feed water, boiler's useful life will be significantly shortened. Resulting from untreated water, the boiler overheats and fails to produce hot water or steam in requisite quantity and results in overall loss of efficiency.
Unconditioned boiler feed water even though coming from a municipal water supply, can contain dissolved salts and form scale on the heat transfer surfaces as the water is heated. This deposited scale drastically reduces the heat transfer of the boiler and leads to overheating, tube failure and efficiency loss. Scale also reduces the flow area, which increases the pressure drop in boiler tubes and piping, resulting in low steam volume and downstream equipment failure. For an effective water treatment programme, one needs to check the boiler water quality from time to time from an outside lab.
- Caustic alkalinity
- Chlorides
- Conductivity
- Dissolved oxygen (DO)
- Iron
- Manganese
- pH
- Reactive silica
- Sulphites
- Total alkalinity
- Total dissolved solids
- Total hardness
- Copper
- Iron
- Total suspended solids
- Turbidity
- Phosphates
- Scales
- Calcium
- ChloridesMagnesium
- Sulphates
- Zinc
It is recommended that water from each source shall be got tested before the commencement of construction work and with appropriate frequency thereafter till the completion of the work. Water used for mixing and curing of concrete needs to be clean and free from detrimental contaminants of alkalis, acids, oils, salts, organic materials, vegetative growth or other substance that may be deleterious to bricks, stone, concrete or steel. Generally potable water is considered satisfactory for mixing. Here are some parameters that are required to be tested as per the standard.
- 0.02 N H2SO4/100ml
- 0.02 N NaOH/100ml
- Chlorides
- Fixed residue
- pH
- Sulphates
- Total suspended solids
- Volatile residue





Cooling towers use evaporative cooling system for controlling process heat. Proper water treatment program is essential for safe operation and life extension of equipment. For an efficient operation of a cooling tower, generally three main factors need to be controlled
- Corrosion
- Scale Formation
- Biological Fouling
As the water evaporates, the dissolved solids originally present in the water remain behind and need to be meticulously controlled, besides bio-contamination. This can lead to corrosion, scale or biological fouling which may negatively affect heat transfer as well as the longevity of system components.
- Calcium hardness
- Chemical oxygen demand (COD)
- Chlorides
- Conductivity
- Iron
- Legionella
- Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP)
- pH
- Reactive silica
- Sulphates
- Sulphides
- Total alkalinity
- Total dissolved solids
- Total hardness
- Total plate count
- Total suspended solids
- Turbidity


Sometimes we face problems with usable water. Water appears cloudy or coloured, plumbing starts corroding faster, water has foul smell or tastes odd, clothes washing starts giving stains or the soap does not foam much. It is the time we must get water checked. More importantly, when the health related problems, especially gastrointestinal illness, are visible, we need to rush water for testing. Here are a few important tests that Polytest Laboratories offer serving all the practical purposes.
- Aluminium
- Ammonical nitrogen
- Arsenic
- Barium
- Boron
- Cadmium
- Calcium
- Chlorides
- Colour
- Detergents
- E.coli
- Fluorides
- Free residual chlorine
- Iron
- Lead
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Mercury
- Mineral oil
- Molybdenum
- Nickel
- Nitrates
- Odour (generic)
- Pesticides
- pH
- Phenolic compounds
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
- Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
- Selenium
- Silver
- Sulphates
- Sulphides
- Total alkalinity
- Total chromium
- Total coliform
- Total dissolved solids
- Total hardness
- Turbidity
- Zinc
The quality of dialysis fluids is too often a neglected problem at many renal healthcare centers. Every week, haemodialysis patients are exposed to about 400 lit water for the production of dialysis fluids which come into direct contact with the bloodstream. It is, therefore, clearly vital to monitor the chemical and microbiological purity of dialysis water. Not only the final dialysis water quality but also the quality of water at various stages of purification system needs to be monitored. As there is always a risk of chemical contamination due to primary pollution of municipal water, whereas the problem of microbiological contamination lies across the stages of entire treatment, distribution and point of use.
- Aluminium
- Arsenic
- Barium
- Cadmium
- Calcium
- Copper
- E.coli
- Fluorides
- Lead
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Mercury
- Nitrates
- Potassium
- Residual chlorine
- Selenium
- Silver
- Sodium
- Standard plate count
- Sulphates
- Total chromium
- Total coliform
- Total dissolved solids
- Total hardness
- Zinc
- Calcium
- Carbonate hardness
- Chlorides
- Copper
- Fluorides
- Iron
- Langelier saturation index (LSI)
- Magnesium
- Nitrates
- Non-carbonate hardness
- Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP)
- pH
- Ryznar stability index (RSI)
- Sulphates
- Total dissolved solids


Packaged drinking water is treated and disinfected water through various treatment and disinfection processes using water from any source. This water is commonly available in jars, bottles and pouches and is sold in retail.
General parameters
- Alkalinity
- Aluminium
- Anionic surface active agents
- Barium
- Boron
- Calcium
- Chlorides
- Copper
- Fluorides
- Free residual chlorine
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Mineral oil
- Nitrates
- Nitrites
- Phenolic compounds
- Selenium
- Sodium
- Sulphates
- Sulphides
- Zinc
Organoleptic & physical parameters
- Colour
- Total dissolved solids
- Turbidity
Toxic substances
- Arsenic
- Cadmium
- Cyanide
- Lead
- Mercury
- Pesticides
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
- Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
- Total chromium
Microbiological paramters
- E.coli
- Faecal streptococci
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Sulphite reducing anaerobes
- Total coliform
- Total viable count
- Vibrio cholera
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Yeast


Water obtained (and packed at natural site) directly from natural source containing natural composition of mineral salts in relative proportions and presence of trace elements. This water is obtained directly from underground sources protected from pollution risks. It is not subjected to any treatment except for mentioned in BIS standards and is packaged close to its emergence of source. BIS standard specifies the composition and levels of minerals, microbiology, organoleptic & physical requirements, toxic, radioactive substances and pesticides. This is a premium quality off the shelf water available in the market.
General parameters
- Alkalinity
- Anionic surface active agents
- Barium
- Boron
- Calcium
- Chlorides
- Copper
- Fluorides
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Mineral oil
- Nitrates
- Nitrites
- Nitrites
- Phenolic compounds
- Selenium
- Sodium
- Sulphates
- Sulphides
- Zinc
Organoleptic & physical parameters
- Colour
- Odour (generic)
- pH
- Total dissolved solids
- Turbidity
Toxic substances
- Arsenic
- Cadmium
- Cyanide
- Lead
- Mercury Pesticides
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
- Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
- Total chromium
Microbiological paramters
- E.coli
- Faecal streptococci
- Mould
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa Salmonella
- Shigella
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Sulphite reducing anaerobes
- Total coliform Vibrio cholera
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Yeast




Water recycling is a key to the sustainable future. It indirectly conserves drinking water used for non-critical applications. Recycled water is effectively used for non-potable purposes, most commonly for agriculture, landscape, parks, industrial cooling and process water, toilet flushing, dust suppression, construction activities, concrete mixing and recharging of artificial lakes.
Wastewater recycling pays as it addresses two problems simultaneously:
ONE: Treatment for compliance and arresting the environmental pollution; and
TWO: utilization of same after purification for a lot many gainful applications saving freshwater costs.
Typical tests for recycled wastewater are those required for statutory compliance with a few additional ones to ensure enhanced quality for recycling purpose.
- Ammonical nitrogen
- Arsenic
- Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)
- Boron
- Cadmium
- Chemical oxygen demand (COD)
- Chlorides
- Copper
- Cyanide
- Fluorides
- Lead
- Mercury
- Nickel
- Percent sodium
- Pesticides
- pH
- Phenolic compounds
- Selenium
- Sulphates
- Sulphides
- Temperature
- Total chromium
- Total dissolved solids
- Total kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN)
- Total oil & grease
- Total residual chlorine
- Total suspended solids
- Zinc


The majority of drinking water at home is derived from various filters and purifiers. Most of the high end purifiers being RO type, the question arises is: Is the purifier removing microorganisms and harmful contaminants? The identification of problem starts with thoroughly testing of RO water. Also RO systems are extensively used in industries for their need of high grade water. Here are some parameters which can be tested for establishing the quality of process water.
- Aluminium
- Arsenic
- Barium
- Cadmium
- Calcium Copper
- E.coli
- Fluorides
- Lead
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Mercury
- Nitrates
- Potassium
- Residual chlorine
- Selenium
- Silt density index (SDI)
- Silver
- Sodium
- Standard plate count
- Sulphates
- Total chromium
- Total coliform
- Total dissolved solids
- Total hardness
- Zinc


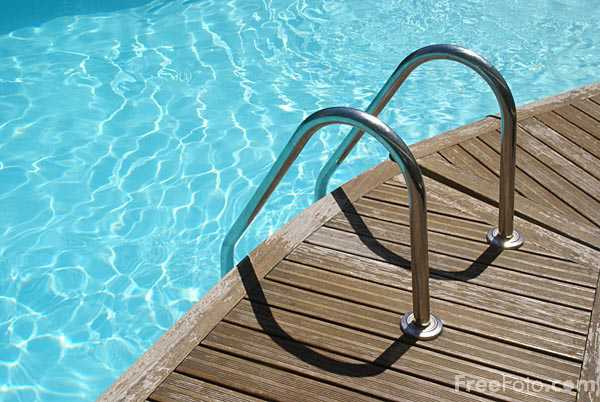
Pool water sanitation is utterly important to ensure healthy conditions in swimming pools or similar recreational water bodies. Proper sanitation is needed to maintain the visual clarity of water and to prevent the transmission of infectious waterborne diseases. Contaminants added up swimmers can influence the pool water management.
Typical contaminants that decrease the water quality include microorganisms from infected users and body oils including sweat, cosmetics, suntan lotion, urine, saliva and fecal matter.
Additionally, the complex reactions between disinfectants and water contaminants can produce a mixture of chloramines and other byproducts. Pathogenic contaminants, i.e. microbes pose greatest hazard to the users leading to recreational water illnesses. Typical pathogens are viruses, bacteria, protozoa and fungi. Diarrhea, Cryptosporidiosis and Giardiasis are the most commonly reported illness associated with pathogenic contaminants, while ear, skin rashes and respiratory infections are also common.
Key to a well maintained pool is timely and thorough testing of feed and pool water.
- Aluminium
- Chlorides
- Coliform MPN
- Colour
- Heavy metals Iron
- Odour (generic)
- Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP)
- Oxygen absorbed
- pH
- Residual chlorine
- Standard plate count
- Total alkalinity
- Total dissolved solids
- Turbidity




The primary functions of metalworking fluids are to reduce the friction between the tool and the material being cut, to dissipate the heat created and to transport chips and swarf away from the cutting zone. Secondary requirements include corrosion protection for the machine and components, controlling foaming, low evaporation and misting, good skin compatibility, high flash point and high stability, etc.
Here are some parameters that indicate the health of the fluid when tested periodically.
Bacterial
- Chlorides
- Copper strip corrosion
- Electrical conductivity
- Floating oil
- Fungal count
- Nitrites
- pH
- Reserve alkalinity
- Total hardness
Chlorides
- Conductivity
- pH
- Reactive silica
- Standard plate count
- Sulphates
- Total dissolved solids
- Total hardness
- Total solids
Grey Water
- Ammonia
- Conductivity
- Faecal coliforms
- Nitrites
- pH
- Sodium
- Sulphates
- Total hardness
- Total kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN)
- Total phosphorus
- Total suspended solids
- Turbidity
- BOD
Distilled Water
- Conductivity
- pH
- Reactive silica
- Total solids
- Colour retention of KMnO4
- Nonvolatile residue
CLIENTS QUESTIONS
Related Question
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium totam rem aperiam eaque ipsa quae illo inventore veritatis quasi architecto beatae.